OpenSIPS #2: Connecting to PSTN
Note: updated for OpenSIPS 2.2 (long term support) on May 10th, 2017.
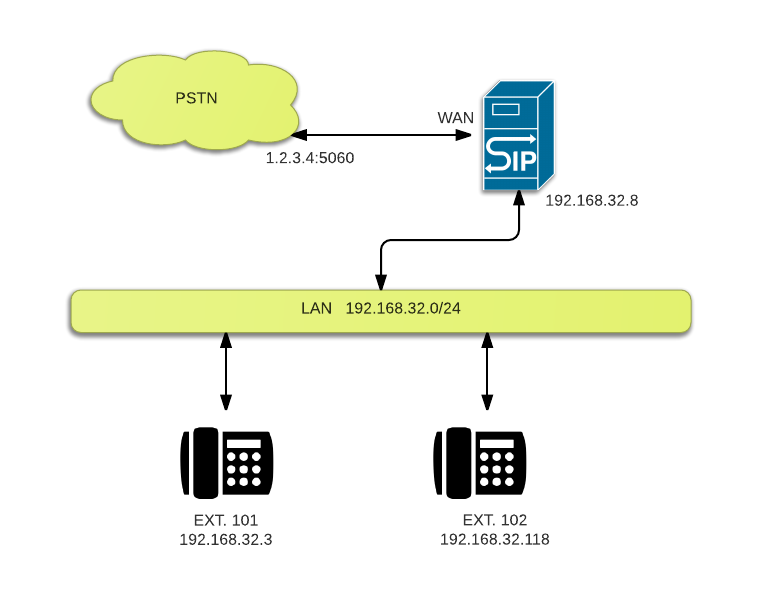
Building on top of the simple example of previous article, we add connectivity to a PSTN gateway. This allows you to make outbound calls from your SIP phone. Since we will be running OpenSIPS on the WAN interface, please keep in mind the security ramifications of doing do, especially since we have no authentication mechanism in place.
Forwarding INVITE’s to the PSTN gateway is actually straight forward. We look the the request user field ($rU) to see if it is a local extension (3 digits). If so, we connect the call as always. If not, we rewrite the IP address ($rd) to that of the gateway and relay the packet.
To our script, we also add a few lines of code to handle sequential requests. This allows us to use loose routing to relay the packets without having to determine the routing logic all over again. Also note the `mhomed=1` and the listen lines at the top of the script. We are not binding to local and WAN interfaces on the server running OpenSIPS.
####### Global Parameters #########
log_stderror=no
log_facility=LOG_LOCAL0
log_level=3
children=2
auto_aliases=no
mhomed=1
listen=udp:192.168.32.8:5060 # LAN Interface
listen=udp:6.7.8.9:5060 # WAN Interface
####### Modules Section ########
mpath="/usr/lib/opensips/modules/"
loadmodule "signaling.so"
loadmodule "sl.so"
loadmodule "registrar.so"
loadmodule "proto_udp.so"
loadmodule "tm.so"
loadmodule "uri.so"
loadmodule "rr.so"
loadmodule "mi_fifo.so"
modparam("mi_fifo", "fifo_name", "/tmp/opensips_fifo")
loadmodule "usrloc.so"
modparam("usrloc", "db_mode", 0)
####### Routing Logic ########
route{
# process sequential requests
if (has_totag()) {
if (!loose_route() && !t_check_trans() ) {
sl_send_reply("404","Not here");
exit;
}
t_relay();
exit;
}
# register user location without authentication
if (method == "REGISTER") {
xlog("registering $tU \n");
save("nuc");
exit;
}
# lookup requested user. if registered, below will replace R-URI with
# registered user's contact. Otherwise forward to PSTN gateway
if (method == "INVITE") {
xlog("calling $tU \n");
if ($rU =~ "^1[0-9][0-9]$") {
if (!lookup("nuc")) {
sl_send_reply("404", "User not found");
exit;
}
} else {
$rd = "1.2.3.4:5060"; # send to gateway
}
}
# make sure this node stays in the communication path
record_route();
# relay request in stateful manner to R-URI
if (!t_relay())
sl_reply_error();
}
When you run the above script, you should be able to make outbound PSTN calls (provided your gateway allows it). You may not have 2-way audio because the gateway has no way of reaching your phone which has a private IP address (read how RTP streams work with SIP). This is a major source of headache in VoIP applications and will be addressed in the next article.